PHLOEM
Basic components of phloem are:
1. Sieve elements
2.Companion cells—–Absent in pteridophytes and gymnosperms.
3.Phloem parenchyma
4. Phloem fibres
A fifth kind of cell type ,the transfer cell has been recently reported in phloem.
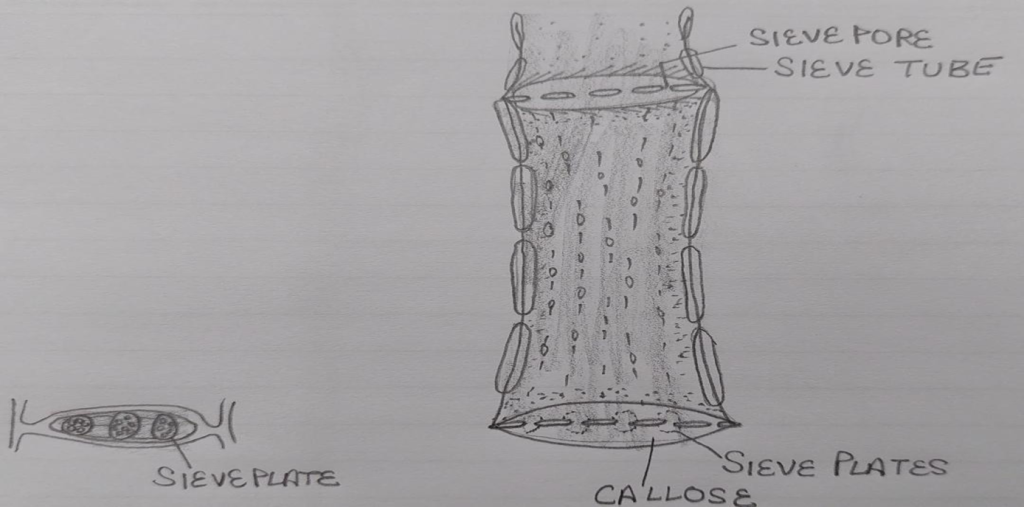
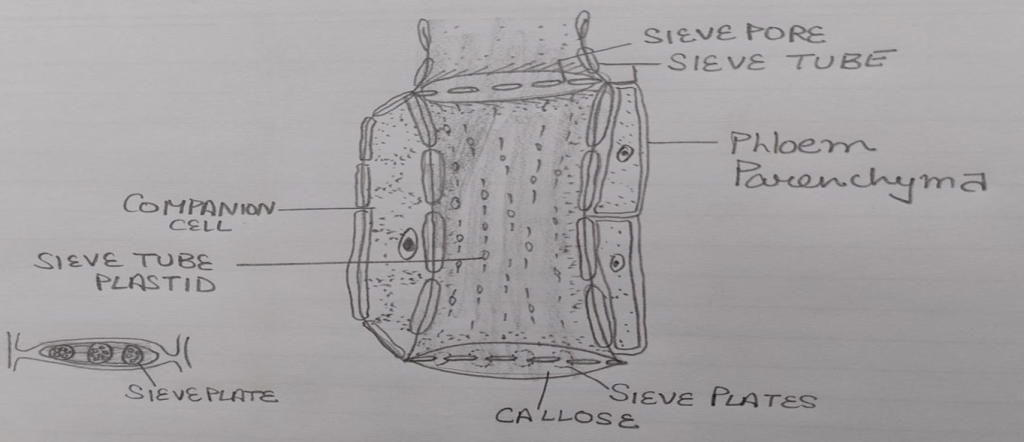
1.Sieve elements: It is the main component of phloem .Sieve elements are placed one above the other to form sieve tubes. Sieve tubes are living cells without nucleus, mitohondria, endoplasmic reticulum and dictyosomes.Cell wall is made up of cellulose , cytoplasm is present enclosing a big central vacuole.
Sieve plates and sieve areas:Group of pores present in the walls of sieve elements are called sieve areas & portion of cross wall possessing sieve areas is called sieve plates.In sieve cells sieve areas are located in the lateral walls where as in sieve tube elements they are located in end walls.
When single sieve plate is present in end walls that is called simple sieve plate and when they are in group then called compound sieve plates.
Function of sieve elements : main function is to translocate the organic material. At end walls there is presence of callose which check the concentration of organic material it dissolve when the solute is dilute and reappear when solute is concentrated to stop its flow.
2.Companion cells: They are living cells and assist the sieve elements. These possess nucleus, ER, dictyosomes, plastid ,ribosomes etc. Cytoplasm is compartmentalized due to presence of membrane system. It also contain slime bodies.Common wall between companion cells and sieve tube elements have pits.They are formed from procambium cells.
3. Phloem parenchyma— Parenchymatous living elongated rounded cells with cellulosic cell wall .They store reserve food material in the form of starch and fats.They are present in pteridophytes and dicot angiosperms & absent in monocots and in some dicots.
4.Phloem fibre: They are non living lignified cells that provide mechanical support to the organ.
