1.First seen by Kollikar in 1880.
2.Named mitochondria by Benda in 1898.
3.Recognised as a site of respiration by Hoogeboom and coworker in 1948.
4. It is known as power house of cell.
•It is found in all aerobic eukaryotic cells and are more concentrated in the more active regions like muscle cells sperm tail etc.
• Mitochondria is absent in mature RBC and in all prokaryotic cells.
STRUCTURE OF MITOCHONDRIA
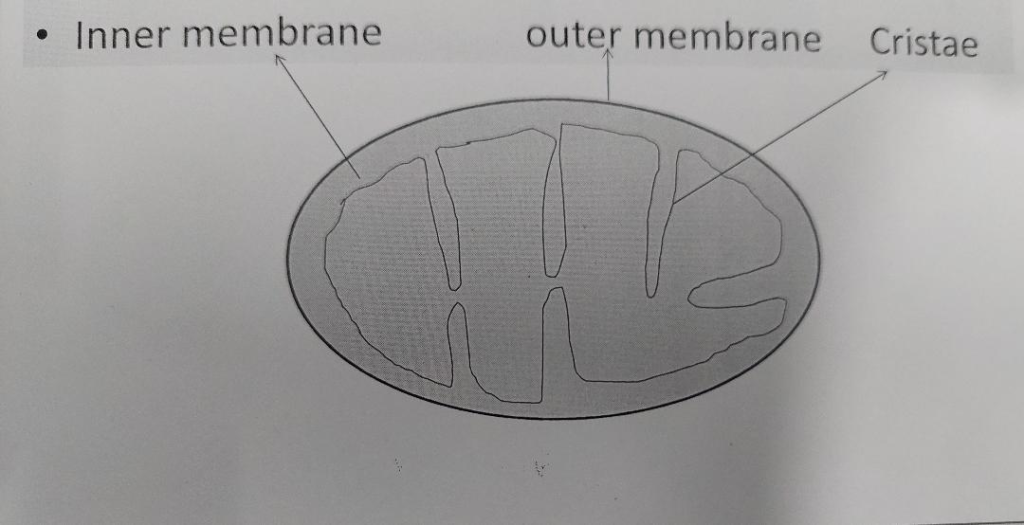
•It is a double membrane organelle the outer membrane is smooth but inner having many folds called cristae which increases the surface area .
| INNER MEMBRANE It is semipermeable hence allow selective movement through it .It has permease protein carrier in it. | OUTER MEMBRANE It is freely permeable and have porin protein channel which allow the free movement. |
•Cristae : The ingrowth ir inner folds of inner membrane are cristae they extends inward in a varying degree and may fuse with the ones from other side so dividing the mitochondria into compartments.they increases the inner surface area of mitochondria to hold the enzymes.
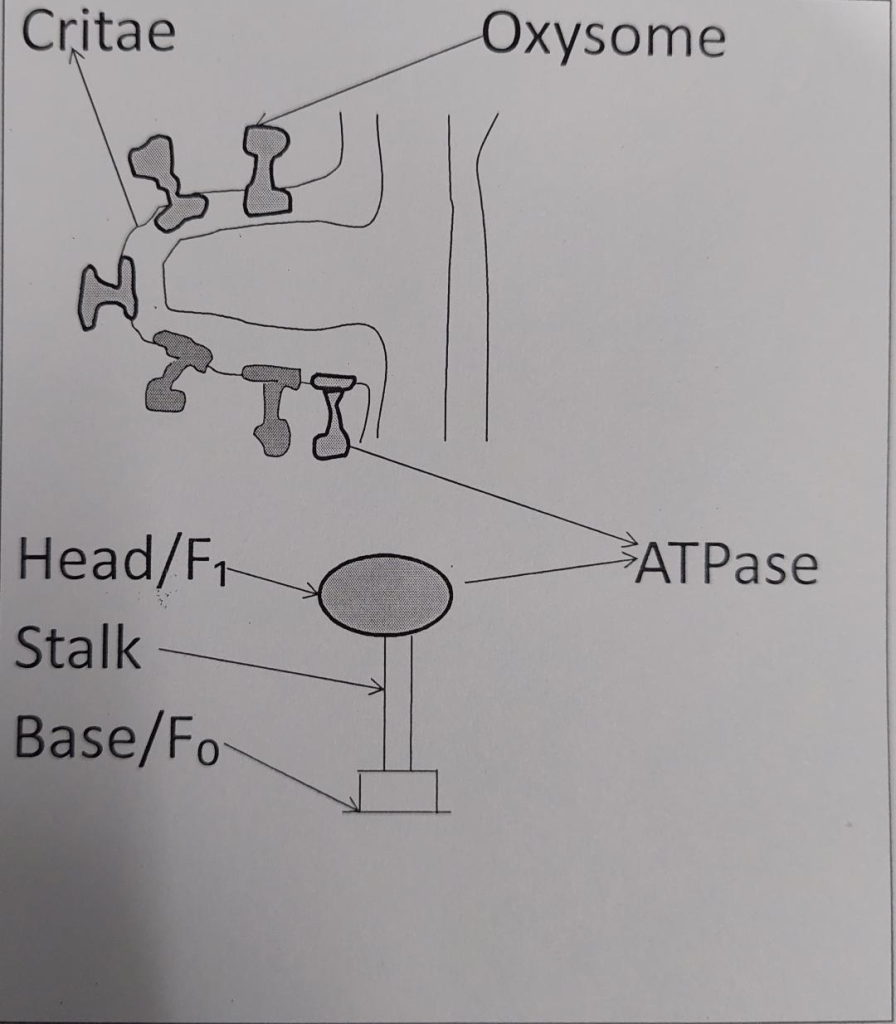
OXYSOMES: Inner membrane bear small lollipop like structure called Oxysomes.
Structure of oxysomes
It consist of three parts: Head piece / F₁ subunit , Stalk, base piece /F₀ subunit. So oxysomes are also called F₀- F₁ complex having ATP synthetase or ATPase enzyme that helps in ATP formation rest of the inner membrane contain the electron carrier molecules of the ETC electron transport chain.