MAIN CHARACTERSTICS OF KINGDOM FUNGI
1.They lack chlorophyll hence do not perform photosynthesis, they are heterotrophic in nature like some are saprophytic ,parasitic ,or some live in symbiotic relationship with algae(lichens) and with roots of higher plants (Mycorrhiza).
2.Cell wall is made up of chitin (having acetyl glucosamine) or cellulose or both.
3. They have definite cell wall nucleus and lack chlorophyll and differentiate vascular bundle.
Basic Structure of Fungi
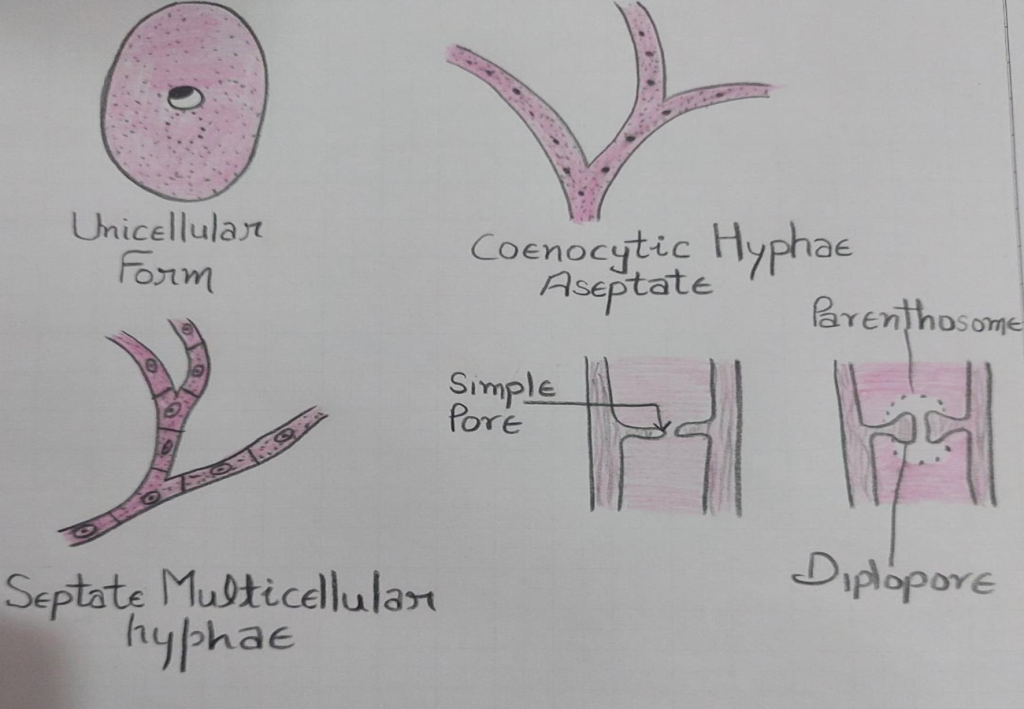
Plectenchyma
•It is of two types:
•1. Prosenchyma: When hyphae are loosely woven and lie parallel to each other.
•2. Pseudoparenchyma: When hyphae are closely packed and cannot be distinguishable easily.
VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION
•1.Fragmentation: Fungal mycelium broken into fragment and each fragment grow to form complete mycelium.
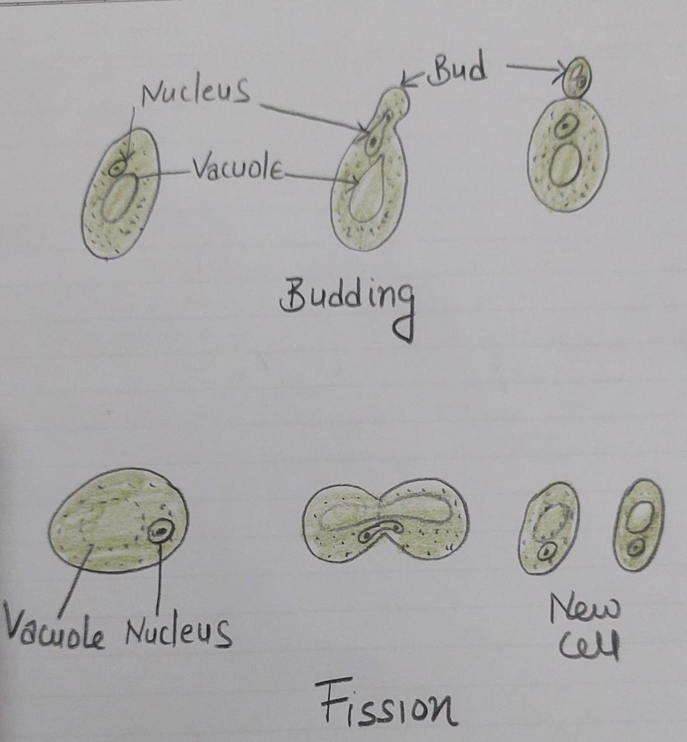
•2.Fission : Single cell divide into two Like in Yeast
•3.Budding :Parent cell produces a bud like outgrowth which after detachment grow into a new cell .Ex. Yeast
•4. Sclerotia:In pseudoparenchyma the outer hyphae become hard and to protect the inner one which germinate in favourable conditions.Ex.Claviceps.
•5.Rhizomorph: In this hyphae interwoven to form cord behave like root and under favourable conditions form new mycelium.
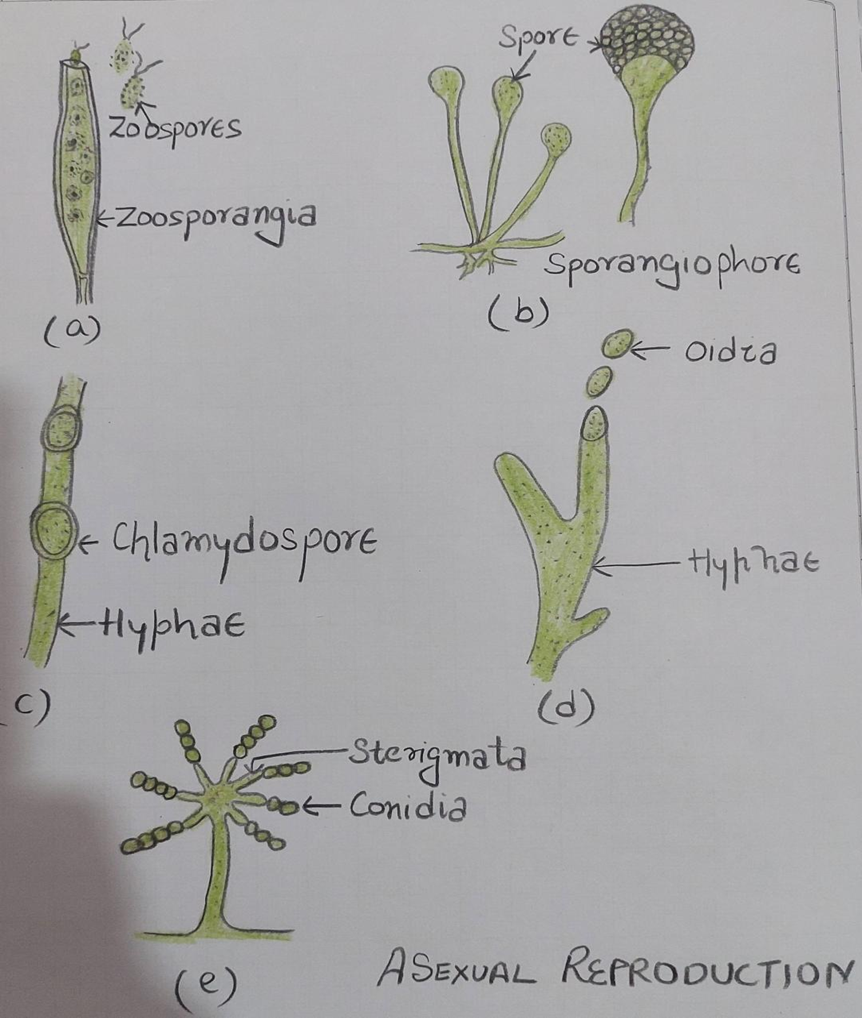
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
1.Zoospores: Motile flagellate without cell wall spores inside zoosporangia Ex. Lower fungi Saprolegnia
2.Sporangiospores: non motile spores inside sporangia. Ex.Rhizopus Mucor.
3. Chlamydospores: Thick walled resting spores directly from hyphae withstand unfavourable conditions.
4.Oidia :Hyphae breakdown into compartments.
5.Conidia : Non motile spores produces singly or in chains on hyphae called conidiophores.
Sexual Reproduction
•It completes in three stages :
•(I) Plasmogamy: In the first stage the cytoplasm of two sex cells fuse together which bring the two nuclei close cell become dikaryon or binucleate.
•(II) Karyogamy: Fusion of two nuclei takes place and the cell become diploid.
•(III) Meiosis: Diploid nuclei divide by meiosis to form haploid nuclei.
•Important points: Sex organ that produces gametes are called Gametangia and male gametangia is called antheridium Female gametangia is called oogonium.
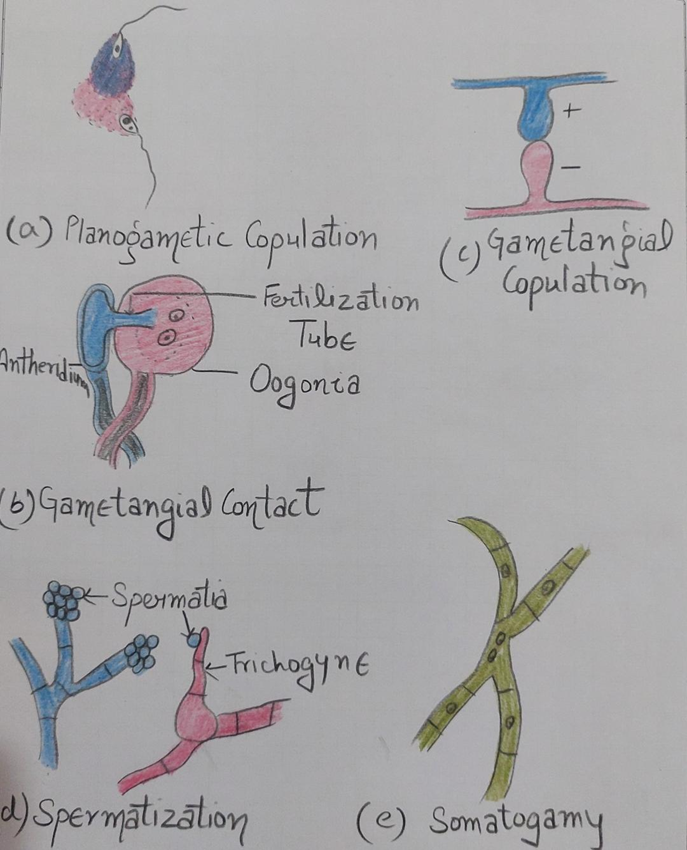
Types of sexual reproduction
1.Planogametic copulation In this one or both the fusing gametes are motile. Ex.Synchytrium
2. Gametangial contact: In this two gametes come close to each other and the male nuclei passes to the female one by fertilization tube.Ex. Phytophthora, Albugo
3.Gametangial copulation: Two gametangia fuses with each other form zygospore. Ex. Mucor ,Rhizopus
4. Spermatization: The spermatia (spore like uninucleated body ) transferred to female gametangia called trichogyne where it transferred its content to the trichogyne by pore.Ex Puccinia graminis
5.Somatogamy: Two vegetative cell fuse Ex . Agaricus