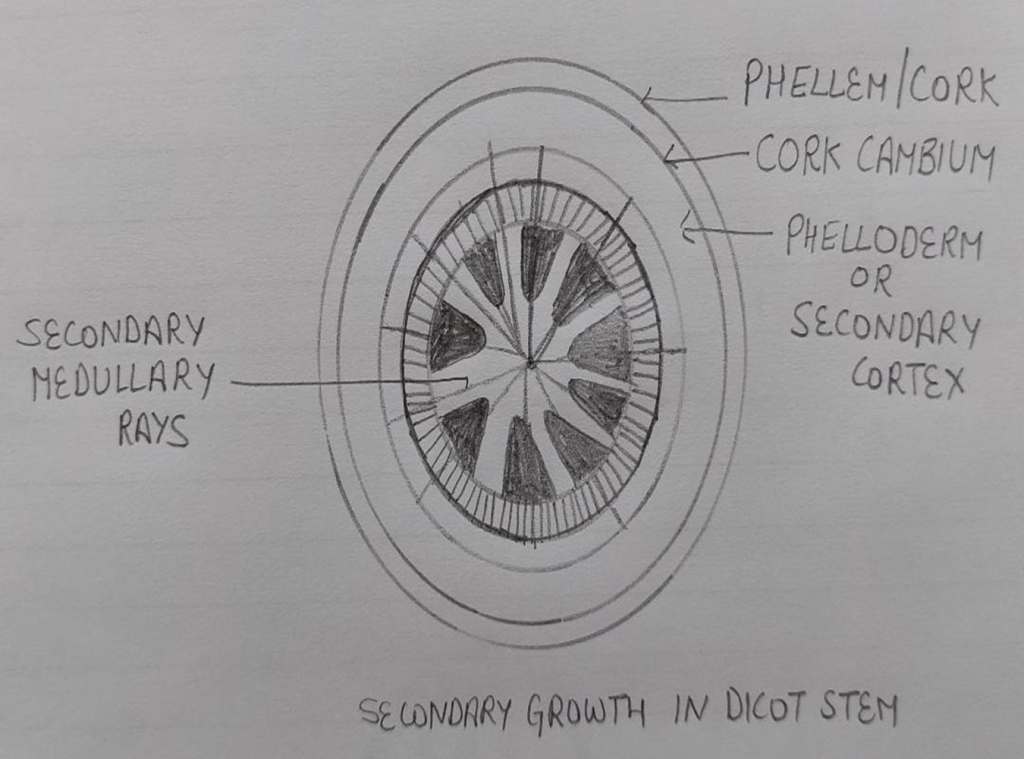
SECONDARY GROWTH IN DICOT STEM
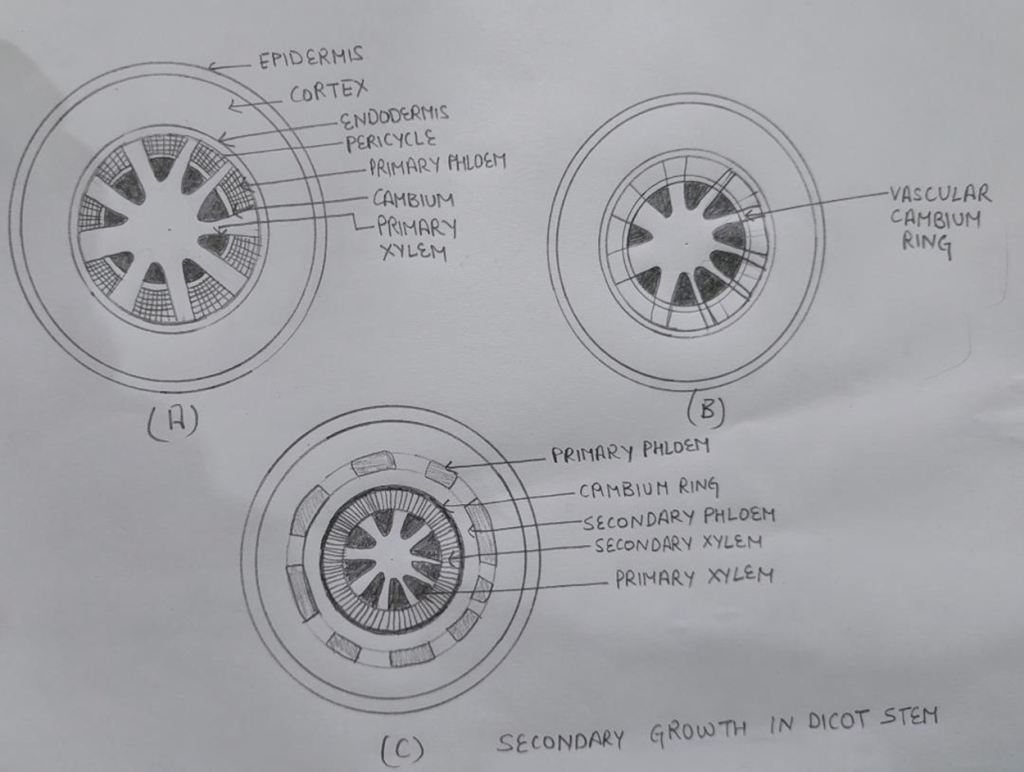
1.FORMATION OF CAMBIUM RING: The cambium present between primary xylem & primary phloem is known as intrafascicular cambium. The parenchymatous cells of medullary rays adjoining the intrafascicular cambium become meristematic and form interfascicular cambium these two cambium form a continuous ring called cambium ring.
2. ACTIVITY OF CAMBIUM RING: Cambium cells divide by periclinal division and add new cells towards innerside as well as towards peripheral side but itself it remain single layered.Toward innerside it add secondary xylem and in radial direction secondary medullary rays & towards periphery it adds secondary phloem .The amound of secondary xylem added is double than secondary phloem because of more growth towards inner side as a result the pressure exerted on outer tissues and the primary phloem gets crushed .
2. Formation of cork cambium: By the addition of secondary phloem and secondary xylem the pressure is exerted on the cortex and epidermis as a result these tissues get crushed and sloughed off . To avoid internal injuries cork cambium ring is developed . It is secondary lateral meristem that develop from epidermis hypodermis cortex and primary phloem cells. Cork cambium this add cork (phellem) towards outer side and secondary cortex towards (phelloderm) towards inner side .Cork, cork cambium and secondary cortex make periderm that give outer protective covering to the stem.