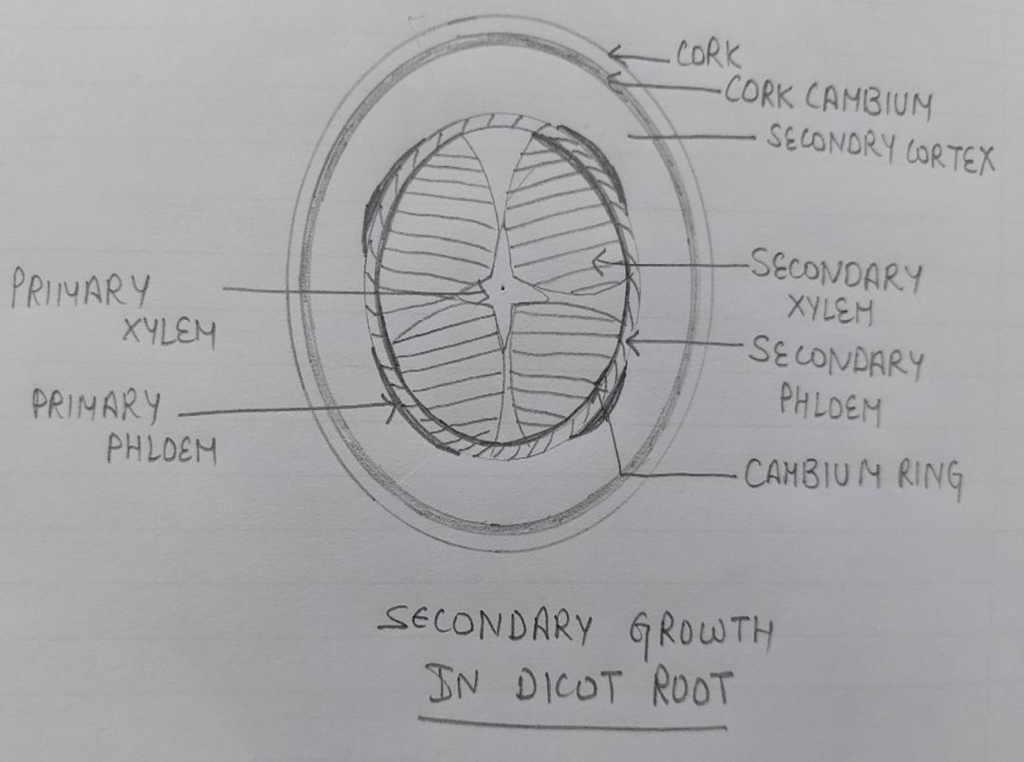
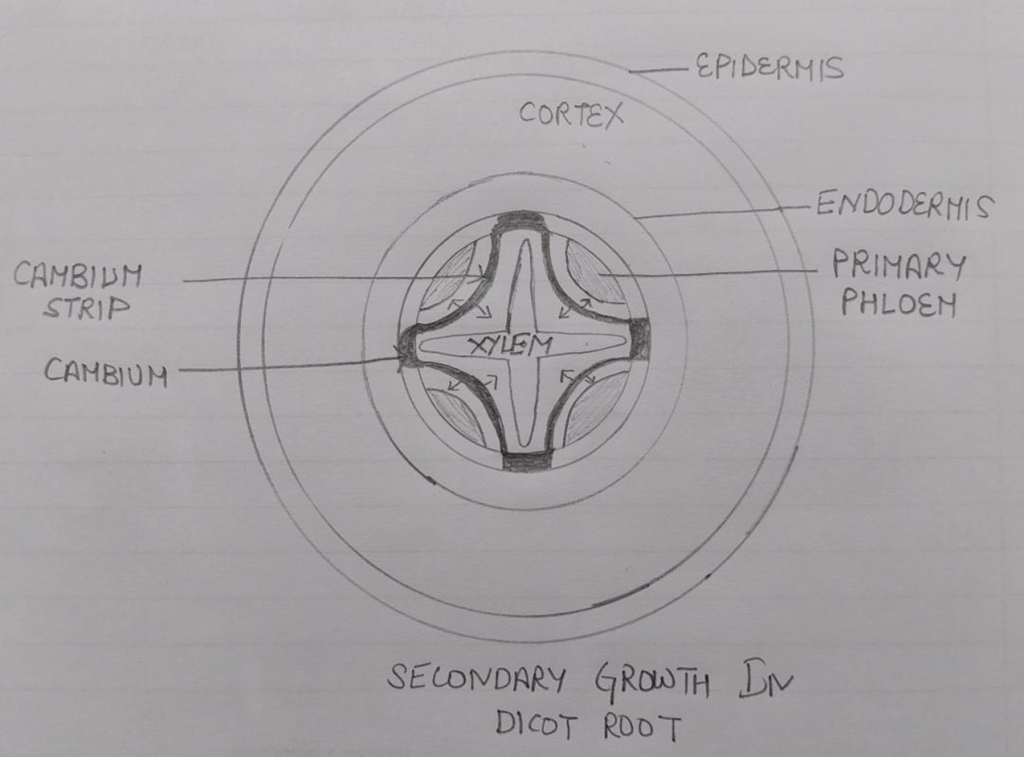
SECONDARY GROWTH IN DICOT ROOT:
Formation of cambium ring:
1.Cambium strips are formed by the activity of parenchymatous cells along the inner edges of primary phloem , The pericycle cells behind the primary xylem to form cambium, now the cambium strips below primary phloem and cambium above the primary xylem joins to form cambium ring , the cells of this ring divide to add secondary xylem towards inner side and secondary phloem towards outer side . The primary xylem remain in its original position but primary phloem is pushed towards outside and crushed.
2. Formation of cork cambium: By the addition of secondary phloem and secondary xylem the pressure is exerted on the cortex and epidermis as a result these tissues get crushed and sloughed off . To avoid the injury of secondary phloem new cambium ring is developed by the division of pericyle cells called cork cambium this add cork (phellem) towards outer side and secondary cortex towards (phelloderm) inner side .Cork, cork cambium and secondary cortex make periderm that give outer protective covering to the root.