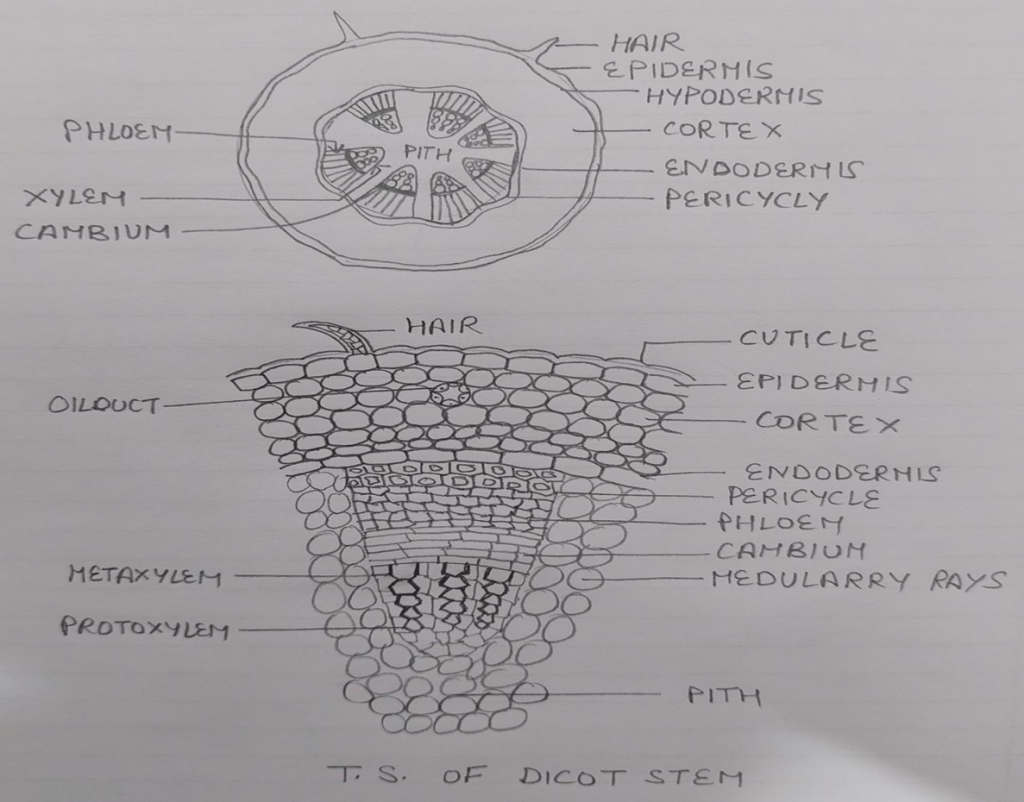
STRUCTURE OF DICOT STEM
EPIDERMIS: Single layered parenchymatous with multicellular glandular hairs or outgrowth covered with cuticle or wax. In young stem stomata are present.
CORTEX: Multilayered thick parenchymatous layer but in some plants it is differentiated into two parts collenchymatous cell layer called hypodermis and rest is parenchymatous cortex.It contain oil ducts.
ENDODERMIS: Innermost layer of thick cells with starch grains casperian strips absent.
PERICYCLE: Found between endodermis and vascular bundle thick and thin walled sclerenchymatous cells .Thick walled cells above primary phloem are called hardblast & thin walled cells are above medullary rays.
VASCULAR SYSTEM: Large no of vascular bundles are present arranged in rings. The vascular bundles are conjoint and open ( vascular cambium is present)and endarch. Collateral in Helianthus,Biclloteral in cucurbita,concentric in Begonia , Rumex etc.
MEDULLARY RAYS: Parenchymatous are between two vascular bundle.
PITH: Large pith occupied by thin parenchymatous cells sometimes hollow cavity.
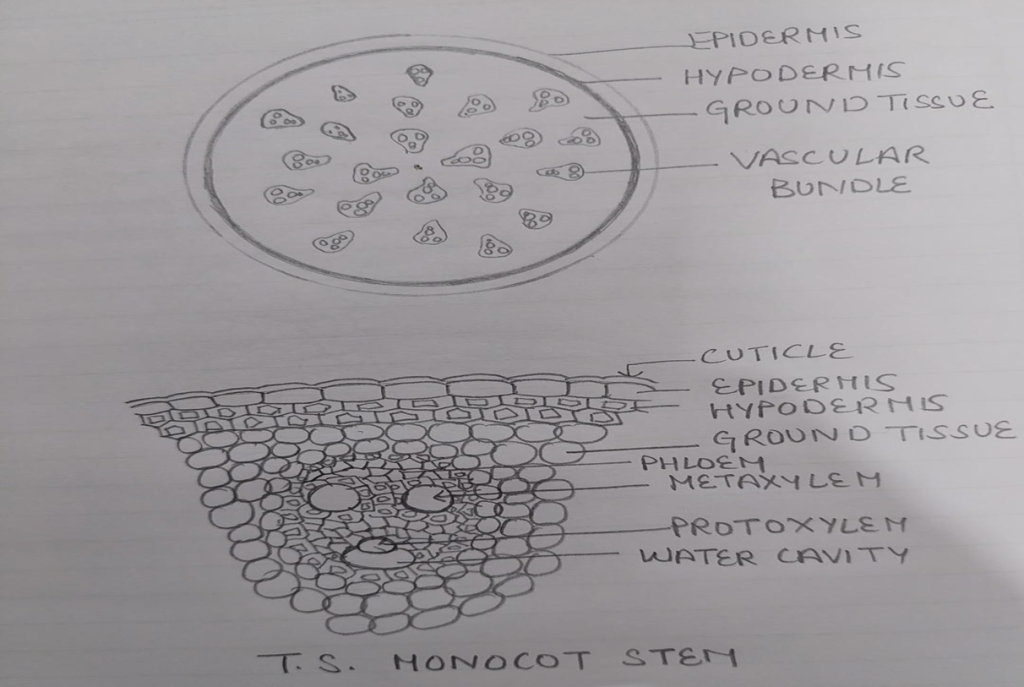
STRUCTURE OF MONOCOT STEM
EPIDERMIS: Single layered protective covering made up of parenchymatous cells covered with cutin , stomata are present but glandular hairs are absent.
HYPODERMIS: Few layered parenchymatous lignified cells provide mechanical strength to the stem.
GROUND TISSUE: In monocots cortex ,endodermis,pericycle ,pith, are absent in place the parenchymatous cells fill the space from hypodermis to the centre this is ground tissue . The cells towards outside are smaller polygonal and compact where as towards centre are large oval & loosely arranged.
•VASCULAR SYSTEM: Numerous vascular bundles scattered in the parenchymatous ground tissue is present in monocots . They are conjoint collateral endarch and closed( vascular cambium is absent).
•CONJOINT: Xylem and phloem in the same radius.
•COLLATERAL: Phloem lies towards outer side and xylem towards inner side.
•ENDARCH: Metaxylem towards periphery protoxylem towards centre
Xylem is Y or V shaped.Water containing lysigenous cavity at the end of protoxylem is present which is formed by dissolution of inner protoxylem vessels and parenchyma.phloem Parenchyma is absent.